고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
728x90
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2917
2917번: 늑대 사냥꾼
첫째 줄에 N과 M (1 ≤ N, M ≤ 500)이 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 N개 줄에는 숲의 지도가 주어진다. 지도에 'V'와 'J'는 딱 하나만 있고, 적어도 하나의 '+'가 있다.
www.acmicpc.net

이 문제는 삽질한 과정이 많아서
풀이를 전부 파보겠습니다.
우선 이 문제에서 구현해야할 것.
1. 나무로부터 거리 구하기
2. 최단경로 구하기
1번은 bfs를 써서 구하면 됩니다.
나무를 deque에 받고
bfs로 거리를 구하면 끝.
문제는 2번인데...
우선 처음에 틀렸던 풀이.
#백준 2817번 늑대사냥꾼
from collections import deque
dx=[0,0,1,-1]
dy=[1,-1,0,0]
N,M=map(int,input().split())
room=[]
tree=deque()
road=[[1e9]*M for _ in range(N)]
for i in range(N):
tmp=list(input().rstrip())
for j in range(M):
if tmp[j]=='+':
tree.append([i,j])
road[i][j]=0
elif tmp[j]=='V':
sx,sy=i,j
elif tmp[j]=='J':
ex,ey=i,j
#트리를 기준으로 각 지점이 트리로부터 얼마나 떨어져있는지 구하기
while tree:
x,y=tree.popleft()
for d in range(4):
nx=x+dx[d]
ny=y+dy[d]
if nx<0 or nx>=N or ny<0 or ny>=M:
continue
if road[nx][ny]>road[x][y]+1:
road[nx][ny]=road[x][y]+1
tree.append([nx,ny])
#늑대이동
visited=[[False]*M for _ in range(N)]
visited[sx][sy]=True
q=deque()
q.append([sx,sy])
answer=road[sx][sy]
while q:
x,y=q.popleft()
if x==ex and y==ey:
continue
go=-1
next=[]
for d in range(4):
nx = x + dx[d]
ny = y + dy[d]
if nx < 0 or nx >= N or ny < 0 or ny >= M:
continue
if visited[nx][ny]==True:
continue
if go<road[nx][ny]:
go=road[nx][ny]
next=[]
next.append([nx,ny])
elif go==road[nx][ny]:
next.append([nx,ny])
if next:
for px,py in next:
visited[px][py]=True
q.append([px,py])
answer=min(answer,go)
print(answer)문제에서 요구한데로
나름 구현한 풀이인데
제출하자마자 틀렸다고 떴습니다.
지금 생각해보니
'현재에서 가장 거리가 큰 걸 간다'
라는 부분으로 틀린 것 같네요.
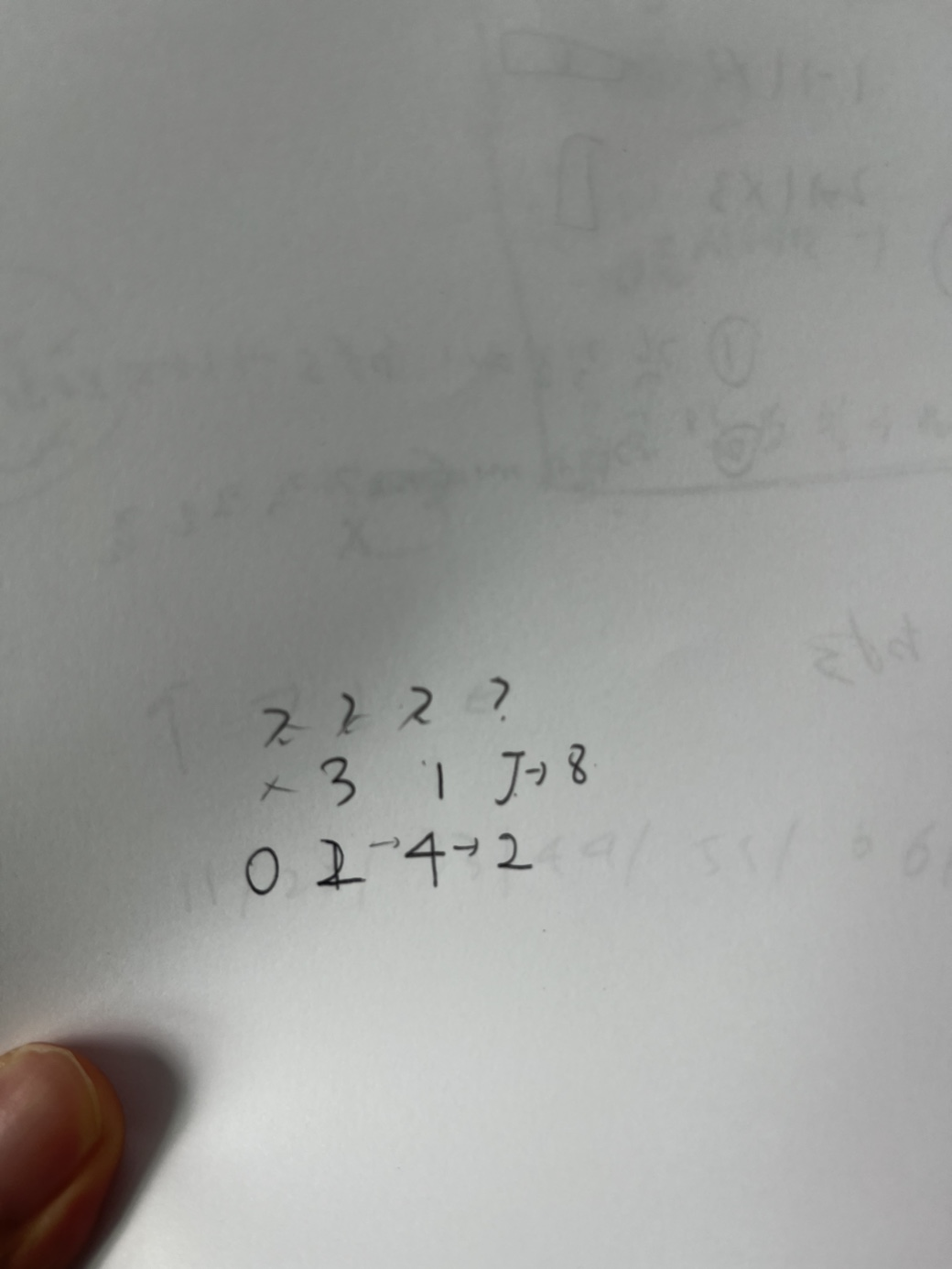
저 코드대로 하면
2에서 3과 4 중에서
4로 이동합니다.
만약 3으로 갔으면
최소거리가 1인 걸 만났을텐데
하필 4로 가는 바람에
최소거리가 2가 되었습니다.
#백준 2817번 늑대사냥꾼
from collections import deque
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**9)
dx=[0,0,1,-1]
dy=[1,-1,0,0]
N,M=map(int,input().split())
room=[]
tree=deque()
road=[[1e9]*M for _ in range(N)]
for i in range(N):
tmp=list(input().rstrip())
for j in range(M):
if tmp[j]=='+':
tree.append([i,j])
road[i][j]=0
elif tmp[j]=='V':
sx,sy=i,j
elif tmp[j]=='J':
ex,ey=i,j
def dfs(x,y,mi):
global answer
if x==ex and y==ey:
answer=max(answer,mi)
return
go=-1
next=[]
for d in range(4):
nx = x + dx[d]
ny = y + dy[d]
if nx < 0 or nx >= N or ny < 0 or ny >= M:
continue
if visited[nx][ny]==True:
continue
if go<road[nx][ny]:
go=road[nx][ny]
next=[]
next.append([nx,ny])
elif go==road[nx][ny]:
next.append([nx,ny])
if next:
m_mi=min(mi,go)
for px, py in next:
visited[px][py] = True
dfs(px,py,m_mi)
visited[px][py]=False
#트리를 기준으로 각 지점이 트리로부터 얼마나 떨어져있는지 구하기
while tree:
x,y=tree.popleft()
for d in range(4):
nx=x+dx[d]
ny=y+dy[d]
if nx<0 or nx>=N or ny<0 or ny>=M:
continue
if road[nx][ny]>road[x][y]+1:
road[nx][ny]=road[x][y]+1
tree.append([nx,ny])
#늑대이동
visited=[[False]*M for _ in range(N)]
visited[sx][sy]=True
answer=0
dfs(sx,sy,1e9)
print(answer)이번엔 dfs방식으로 풀어쓴 방식.
하지만 이건 재귀함수를 너무 많이 돌아야해서
메모리 초과가 발생했습니다.
결국 구글링으로 힌트를 얻은 방식은
다익스타알고리즘.
여기서는 최대힙을 써야합니다.
파이썬에는 최소 힙이 되어있기 때문에
맨 앞을 음수로 바꾸면 끝.
#백준 2817번 늑대사냥꾼
from collections import deque
from heapq import heappop,heappush
dx=[0,0,1,-1]
dy=[1,-1,0,0]
N,M=map(int,input().split())
room=[]
tree=deque()
road=[[1e9]*M for _ in range(N)]
for i in range(N):
tmp=input().rstrip()
for j in range(M):
if tmp[j]=='+':
tree.append([i,j])
road[i][j]=0
elif tmp[j]=='V':
sx,sy=i,j
elif tmp[j]=='J':
ex,ey=i,j
#트리를 기준으로 각 지점이 트리로부터 얼마나 떨어져있는지 구하기
while tree:
x,y=tree.popleft()
for d in range(4):
nx=x+dx[d]
ny=y+dy[d]
if nx<0 or nx>=N or ny<0 or ny>=M:
continue
if road[nx][ny]>road[x][y]+1:
road[nx][ny]=road[x][y]+1
tree.append([nx,ny])
#늑대이동
q=[]
heappush(q,[-road[sx][sy],road[sx][sy],sx,sy])
visited=[[False]*M for _ in range(N)]
visited[sx][sy]=True
answer=0
while q:
now_dis,level,x,y=heappop(q)
if x==ex and y==ey:
answer=max(answer,level)
break
for d in range(4):
nx = x + dx[d]
ny = y + dy[d]
if nx < 0 or nx >= N or ny < 0 or ny >= M:
continue
if visited[nx][ny]==True:
continue
visited[nx][ny]=True
heappush(q,[-road[nx][ny],min(level,road[nx][ny]),nx,ny])
print(answer)
파이썬으로 최대힙을 이렇게 쓸 수 있구나를 공부하면서
경로에 대한 학습을 해볼 수 있는 좋은 문제였습니다.
728x90
'알고리즘 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 16724번] 피리 부는 사나이(파이썬) (1) | 2022.09.14 |
|---|---|
| [백준 12946번] 육각보드(파이썬) (1) | 2022.09.14 |
| [백준 14947번] 상자배달 (0) | 2022.09.13 |
| [백준 25208번] 새벽의 탐정(파이썬) (1) | 2022.09.12 |
| [백준 14948] 군대탈출하기(파이썬) (0) | 2022.09.11 |





댓글 영역